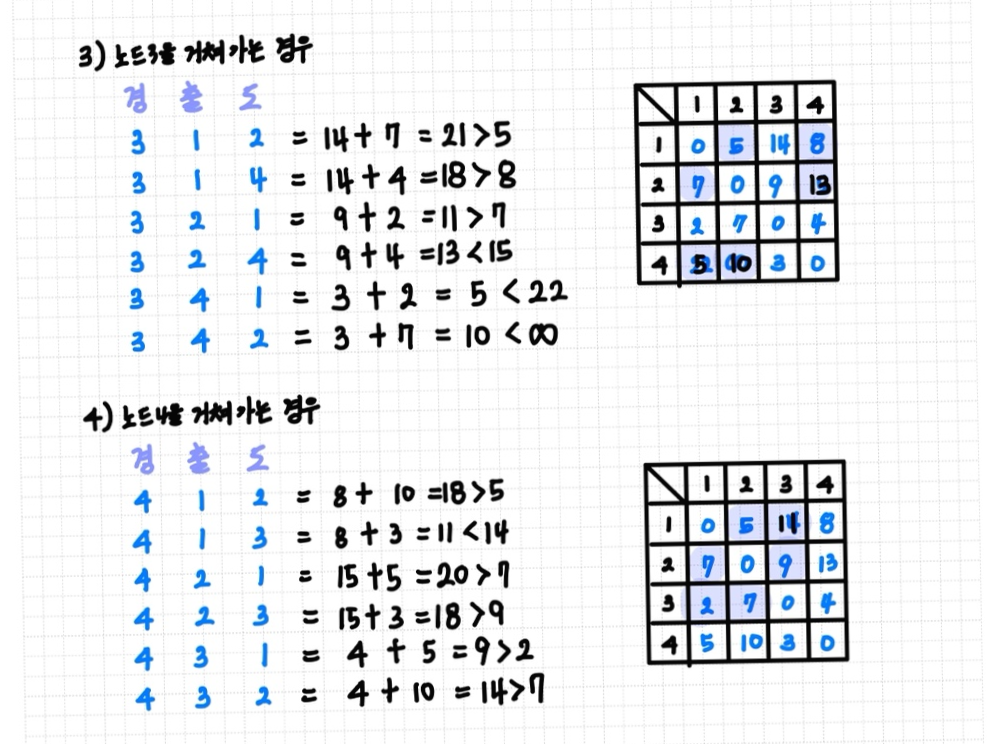
최소신장트리(MST)란?
- 무향 가중치 그래프에서 신장트리를 구성하는 간선들의 가중치 합이 최소인 신장트리
- Kruskal 알고리즘
- Prim 알고리즘
Kruskal
- 간선을 하나씩 선택해서 MST를 찾는 알고리즘
- 모든 간선을 가중치에 따라 오름차순 정렬
- 가중치가 낮은 순서대로 간선을 선택하며 사이클이 발생하지 않도록 간선 선택
- N-1개의 간선이 선택될 때까지 2번 반복 수행

- 코드
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
|
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.StringTokenizer;
public class Kruskal {
static class Edge implements Comparable<Edge>{
int start, end, weight;
public Edge(int start, int end, int weight) {
this.start = start;
this.end = end;
this.weight = weight;
}
@Override
public int compareTo(Edge o) {
return this.weight-o.weight;
}
}
static int V,E,A,B,C;
static int [] parents;
static Edge[] edgeList;
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
StringTokenizer st;
st = new StringTokenizer(br.readLine()," ");
V = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken());
E = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken());
parents = new int[V+1];
edgeList = new Edge[E];
for(int i=0;i<E;i++) {
st = new StringTokenizer(br.readLine()," ");
A = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken());
B = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken());
C = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken());
edgeList[i] = new Edge(A,B,C);
}
make();
Arrays.sort(edgeList);
int result = 0, count=0;
for(Edge edge : edgeList){
if(union(edge.start,edge.end)){ // 싸이클이 발생하지 않았으면
result += edge.weight;
count++;
if(count == V-1){ // 연결 간선수가 정점수-1이면 다 연결
break;
}
}
}
System.out.println(result);
}
public static void make() {
for(int i=0;i<V;i++) parents[i]= i;
}
public static boolean union(int a, int b) {
int aRoot = find(a);
int bRoot = find(b);
if(aRoot != bRoot) {
parents[bRoot] = aRoot;
return true;
}
return false;
}
public static int find(int x) {
if(parents[x]==x) return x;
return parents[x]= find(parents[x]);
}
}
|
cs |
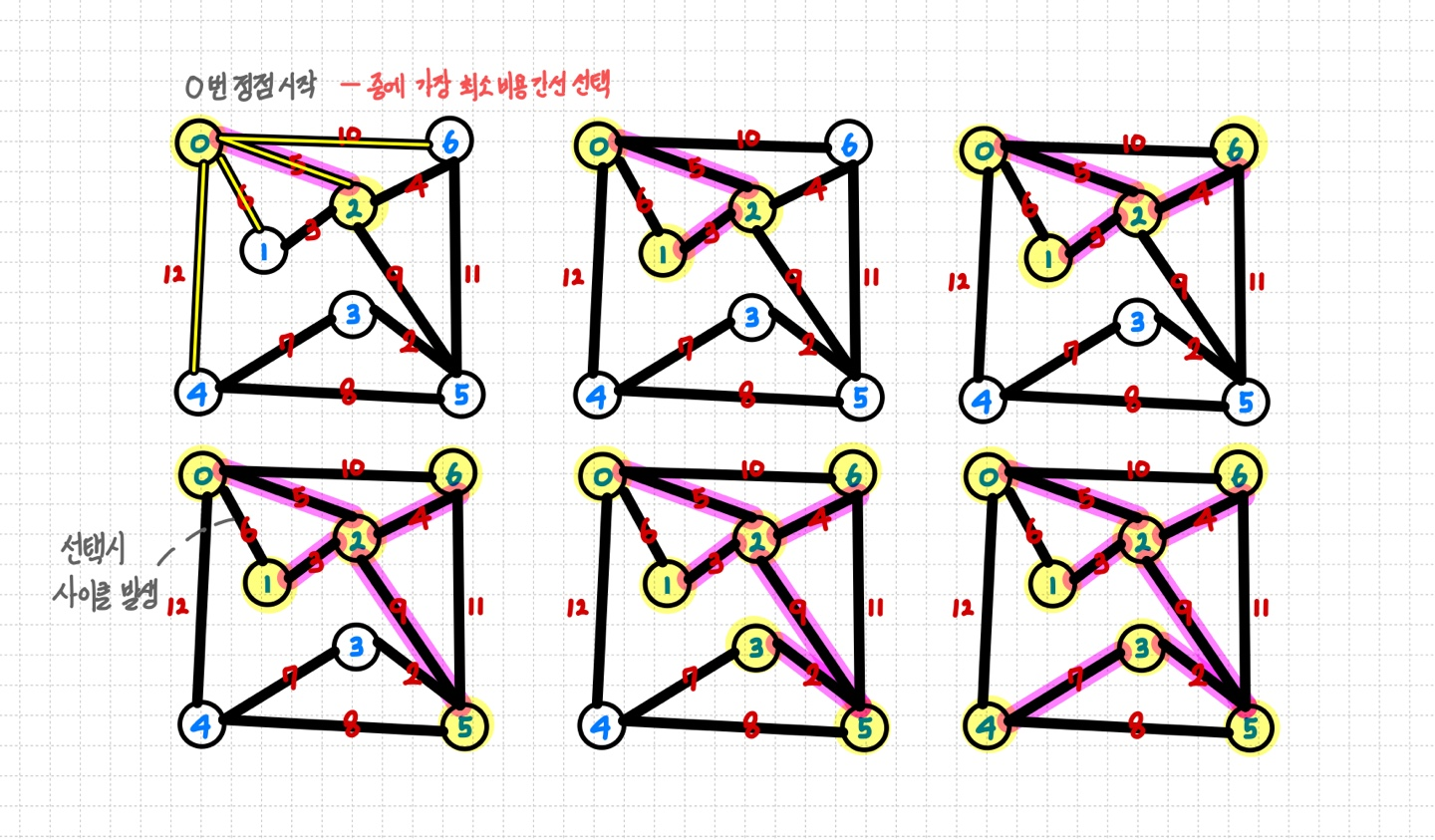
Prim
- 하나의 정점에서 연결된 간선들 중에 하나씩 선택하면서 MST를 만들어가는 방식
- 임의 정점을 하나 선택
- 선택한 정점과 인접하는 정점들 중에 최소 비용 간선이 존재하는 장점 선택
- 모든 정점이 선택될 때 까지 1, 2번 반복
- 코드
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
|
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.StringTokenizer;
public class Prim{
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
int N = Integer.parseInt(br.readLine().trim());
int[][] input = new int[N][N];
boolean[] visited = new boolean[N];
int[] minEdge = new int[N];
StringTokenizer st;
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) {
st = new StringTokenizer(br.readLine());
for (int j = 0; j < N; j++) {
input[i][j] = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken());
}
minEdge[i] = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
}// i노드에서 j노드까지의 비용을 모두 배열에 저장
int minVertex,min,result = 0;
minEdge[0] = 0; // 임의의 시작점 비용 0 셋팅
for(int c = 0 ; c< N; c++){// 모든 정점 수만큼 반복
min = Integer.MAX_VALUE;// 초기값으로 정수의 최대치를 주고 시작
minVertex = 0;
for(int i=0; i<N; ++i) {
if(!visited[i] && min > minEdge[i] ) {
min = minEdge[i];
minVertex = i;
}
}
result += min;
visited[minVertex] = true;
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) {
if (!visited[i] && input[minVertex][i] != 0 && minEdge[i] > input[minVertex][i] ) {
minEdge[i] = input[minVertex][i];
}
}
}
System.out.println(result);
}
}
|
cs |
'정리 > 자료구조+알고리즘' 카테고리의 다른 글
| 이진 탐색 (Binary Search) 알고리즘 (0) | 2021.07.05 |
|---|---|
| 세그먼트 트리(Segment Tree) (0) | 2021.07.01 |
| 위상정렬 (0) | 2021.06.18 |
| 비트마스크 (BitMask) (0) | 2021.04.21 |
| Floyd Warshall (플로이드 와샬) 알고리즘 (0) | 2021.03.25 |